什么是MCP?
MCP,全称Model Context Protocol (模型上下文协议),是由 Anthropic(Claude 模型的开发者)于 2024 年 11 月推出并开源的一种标准化通信协议。
MCP架构
CS架构
MCP 客户端(Client):通常是大模型所在的应用程序(如ClaudeDesktop、Cursor),负责发起请求
MCP 服务器(Server):一个轻量级服务,连接特定的外部数据源或工具,通过MCP协议提供标准化的访问接口
通信方式
JSON-RPC2.0协议
本地stdio传输
远程HTTP+SSE传输
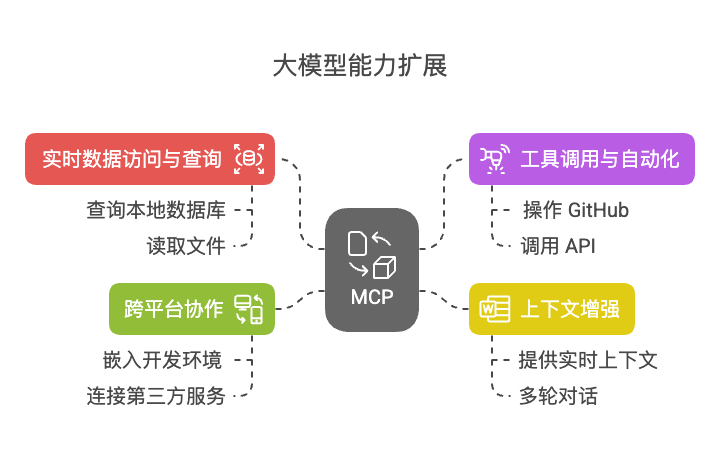
MCP 能做什么? MCP的主要作用是扩展大模型的能力,统一Function Calling规范,实现了大模型从”只会聊天”到”能干活的智能助手”升级。
应用场景
实时数据访问与查询
查询本地数据库:如分析 SQLite 中的销售数据
读取文件:总结 PDF 文档或整理会议记录
工具调用与自动化
操作 GitHub:创建 Issue、提交 PR
调用 API:获取天气、发送邮件、查询股票
上下文增强
提供实时上下文:基于最新数据生成准确回答
多轮对话:动态管理上下文,确保连贯性
跨平台协作
嵌入开发环境:在 IDE 中调用工具或查询数据
连接第三方服务:如 Slack、Notion
开发者如何使用 MCP? 开发者可以通过 MCP 协议创建服务端或客户端,扩展大模型的功能。以下是基本步骤:
核心组件 MCP 服务器可以提供三种功能:
Resources:类文件数据,如文件内容或 API 响应。
Tools:可执行函数,如计算或查询服务。
Prompts:预定义模板,辅助大模型完成任务。
开发流程
开发 MCP 服务器
使用 SDK(如 Python 的 mcp 库)定义工具或资源
启动服务,支持 stdio 或 HTTP 传输
开发或配置客户端
连接服务器,调用工具或资源
可集成到现有工具(如 Cursor)
测试与调试:
案例:实现实时天气查询的MCP服务 使用 MCP 实现一个天气查询服务,包括服务端和客户端
前置条件
环境依赖:pip install -r requirements.txt
天气API密钥:注册高德开放平台 ,生成应用APP_ID
环境:Python 3.8+
MCP 服务端 服务端提供天气查询工具 query_weather,通过 高德开放平台 API 获取3天内的数据
服务配置文件: .env 1 2 3 HOST=0.0.0.0 PORT=8882 API_KEY=""
安装依赖:pip install -r requirements.txt 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 annotated-types==0.7.0 anyio==4.9.0 certifi==2025.1.31 click==8.1.8 fastapi==0.115.12 h11==0.14.0 httpcore==1.0.7 httpx==0.28.1 httpx-sse==0.4.0 idna==3.10 mcp==1.6.0 pydantic==2.11.2 pydantic-settings==2.8.1 pydantic_core==2.33.1 python-dotenv==1.1.0 sniffio==1.3.1 sse-starlette==2.2.1 starlette==0.46.1 typing-inspection==0.4.0 typing_extensions==4.13.1 uvicorn==0.34.0
代码:weather_server.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCPimport httpxfrom dotenv import load_dotenvimport osload_dotenv() def get_env_config (): config = { 'API_KEY' : os.getenv('API_KEY' ), 'HOST' : os.getenv('HOST' , '0.0.0.0' ), 'PORT' : int (os.getenv('PORT' , 8882 )) } return config mcp = FastMCP("weather" , description="实时天气查询服务" , host=get_env_config().get("HOST" , "0.0.0.0" ), port=get_env_config().get("PORT" , 8882 )) @mcp.tool() def query_weather (city_code: str ) -> str : """查询指定城市的实时天气。 Args: city_code: 城市名称编码,例如 'Beijing' 110000 Returns: 天气信息的字符串描述 """ api_key = get_env_config().get("API_KEY" ) url = f"https://restapi.amap.com/v3/weather/weatherInfo?key={api_key} &city={city_code} &extensions=all" try : response = httpx.get(url) response.raise_for_status() data = response.json() forecast = data["forecasts" ][0 ] city_name = forecast["city" ] weather_info = forecast["casts" ][0 ] temp_day = weather_info["daytemp" ] description = weather_info["dayweather" ] return f"{city_name} 的天气:{description} ,白天温度 {temp_day} °C" except httpx.HTTPError as e: return f"查询失败:{str (e)} " except (KeyError, IndexError): return "查询失败:无法解析天气数据" if __name__ == "__main__" : mcp.run(transport="sse" )
运行MCP服务端 命令:python weather_server.pyhttp://0.0.0.0:8882
MCP客户端 客户端通过 MCP 调用服务端工具,并提供HTTP接口供外部访问
代码:weather_client_with_api.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import asyncioimport httpxfrom fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPExceptionfrom mcp import ClientSessionfrom mcp.client.sse import sse_clientimport uvicornfrom dotenv import load_dotenvimport osload_dotenv() API_KEY = os.getenv("API_KEY" ) app = FastAPI(title="天气查询MCP客户端" ) MCP_SERVER_URL = "http://127.0.0.1:8882/sse" async def get_city_code (city_name: str ) -> str : """通过高德行政区划查询 API 将城市名称转换为城市代码""" url = f"https://restapi.amap.com/v3/config/district?key={API_KEY} &keywords={city_name} &subdistrict=0" async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client: response = await client.get(url) response.raise_for_status() data = response.json() if data["status" ] == "1" and data["districts" ]: return data["districts" ][0 ]["adcode" ] else : raise ValueError(f"无法找到城市 {city_name} 的代码" ) async def query_weather_from_mcp (city_name: str ) -> str : """查询天气,先将城市名称转换为代码,再调用 MCP 服务端""" try : city_code = await get_city_code(city_name) print (f"城市 {city_name} 的代码: {city_code} " ) async with sse_client(MCP_SERVER_URL) as (reader, writer): async with ClientSession(reader, writer) as session: await session.initialize() result = await session.call_tool("query_weather" , {"city_code" : city_code}) print (f"result 类型: {type (result)} " ) print (f"result 内容: {result} " ) if result.content and len (result.content) > 0 : return result.content[0 ].text else : raise ValueError("未收到有效天气数据" ) except Exception as e: raise ValueError(f"查询天气失败: {str (e)} " ) @app.get("/weather/{city}" async def get_weather (city: str ): try : weather_result = await query_weather_from_mcp(city) return {"city" : city, "weather" : weather_result} except Exception as e: print (f"错误详情:{str (e)} " ) raise HTTPException(status_code=500 , detail=f"查询失败:{str (e)} " ) if __name__ == "__main__" : uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0" , port=8080 )
运行客户端 命令:python weather_client_with_api.pyhttp://localhost:8080
测试
启动服务端
1 python weather_server.py
启动客户端:
1 python weather_client_with_api.py
调用接口:
1 curl http://localhost:8080/weather/北京
输出:
1 2 3 4 { "city": "北京", "weather": "北京市 的天气:小雨,白天温度 22°C" }
工作流程
外部请求到达客户端的 /weather/北京 接口
客户端通过MCP协议调用服务端的query_weather工具
服务端查询高德天气API,返回天气数据
客户端将结果以JSON格式返回给调用者
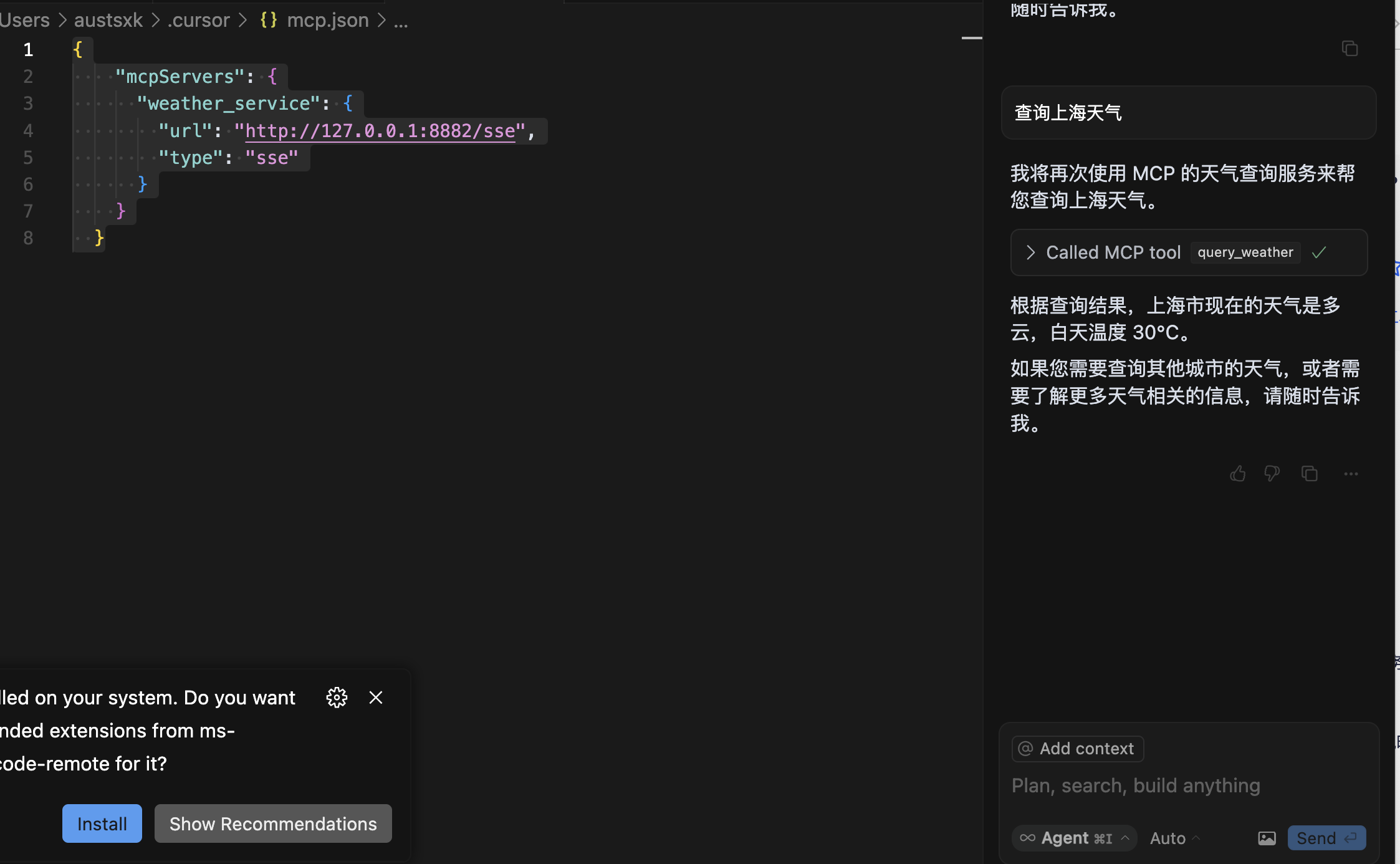
集成到MCP到Cursor
增加MCP server
设置 –>MCP –>新增MCP服务 –>保存 –>重启Cursor 配置信息(mcp.json)如下 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 { "mcpServers": { "weather_service": { "url": "http://127.0.0.1:8882/sse", "type": "sse" } } }
Chat模式下使用MCP
结果
MCP 的优势与未来 优势
通用性:支持多种模型和平台,基于 JSON-RPC 2.0
灵活性:支持本地和远程传输,适配不同场景
安全性:内置授权机制,确保工具调用安全
社区支持:开源协议,GitHub 上已有丰富生态
未来展望 随着 MCP 的普及,我们可以期待:
更多预构建的 MCP 服务器(如 GitHub、Notion 集成)
大模型与开发工具的深度融合
跨设备、跨平台的 AI 协作生态
总结 MCP 是大模型与外部世界连接的桥梁,通过标准化协议提升了AI的实用性和扩展性。无论是查询天气、管理代码,还是自动化任务,MCP都为开发者提供了强大支持。